Unveiling the Transcendent Beauty: Malevich and the Russian Avant-Garde
Unveiling the Transcendent Beauty Introduction:Entering the realm of Kazimir Malevich and the Russian Avant-Garde is akin to embarking on a spiritual odyssey of artistic revelation. As an impassioned collector deeply enamored by Malevich’s oeuvre, one finds oneself irresistibly drawn to the ineffable allure and profound philosophical depths that characterize each stroke of his brush. In this essay, the narrative unfolds from the perspective of an ardent collector, eager to convey the enrapturing essence of Malevich’s graphic works, offering glimpses into the transcendent beauty that continues to captivate collectors and aficionados worldwide. The Russian Avant-Garde Movement:For those enthralled by the enigmatic allure of Malevich’s creations, the Russian Avant-Garde movement stands as…
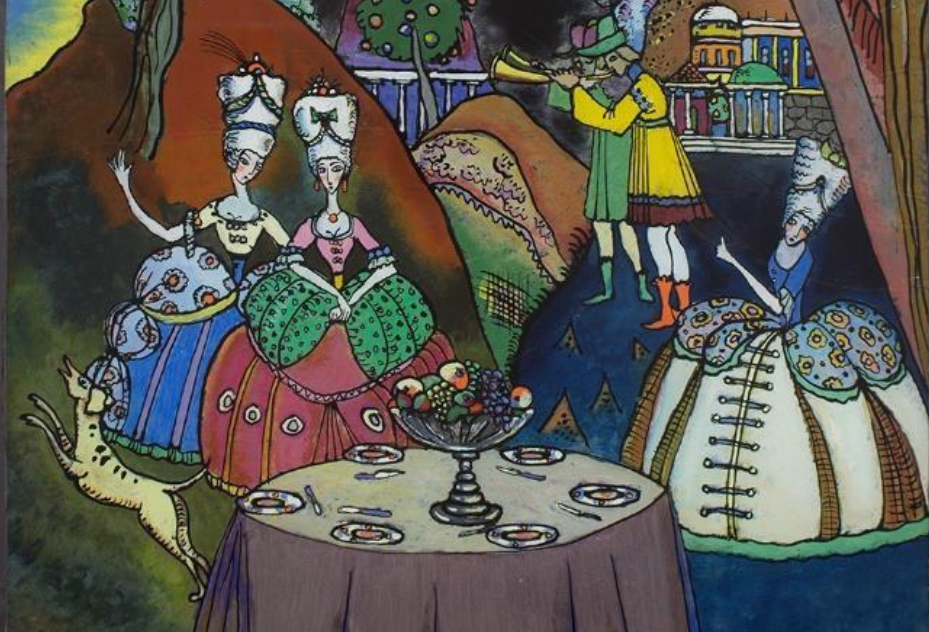
Why is Wassily Kandinsky “The Rider” (1909) an important work?
Why is Wassily Kandinsky “The Rider” (1909) an important work? Around 1910, Kandinsky’s artistic style began to shift significantly towards abstraction. In 1910, he completed his first truly abstract watercolor, marking a pivotal moment in his career. This period also saw the publication of his influential book “Concerning the Spiritual in Art” in 1910, where he explored the spiritual dimensions of art and its connection to music. Kandinsky’s notable works from this era include “Composition I” (1910), which was unfortunately destroyed during World War II. His paintings increasingly emphasized emotion through color and form, moving away from traditional representation. In 1911, he co-founded the influential group Der Blaue Reiter, further…
Why would Kazimir Malevich shift away from Suprematism after the 1920’s?
Kazimir Malevich’s evolving relationship with Suprematism in the post-1920s era was influenced by a variety of factors, reflecting a complex interplay of political, personal, and philosophical dynamics. Politically, the ascent of Joseph Stalin’s regime in Soviet Russia marked a significant shift in cultural policies, favoring Socialist Realism as the sanctioned artistic style. Suprematism’s abstract, non-representational approach clashed with the regime’s preference for art that served propagandistic purposes and depicted idealized Soviet themes. Consequently, Malevich encountered mounting challenges in showcasing and disseminating his Suprematist works within the state-controlled artistic milieu. However, Malevich’s relationship with Suprematism was not solely defined by external pressures. Internally, he experienced a gradual evolution of his artistic…