Understanding Suprematism: Malevich’s Radical Vision
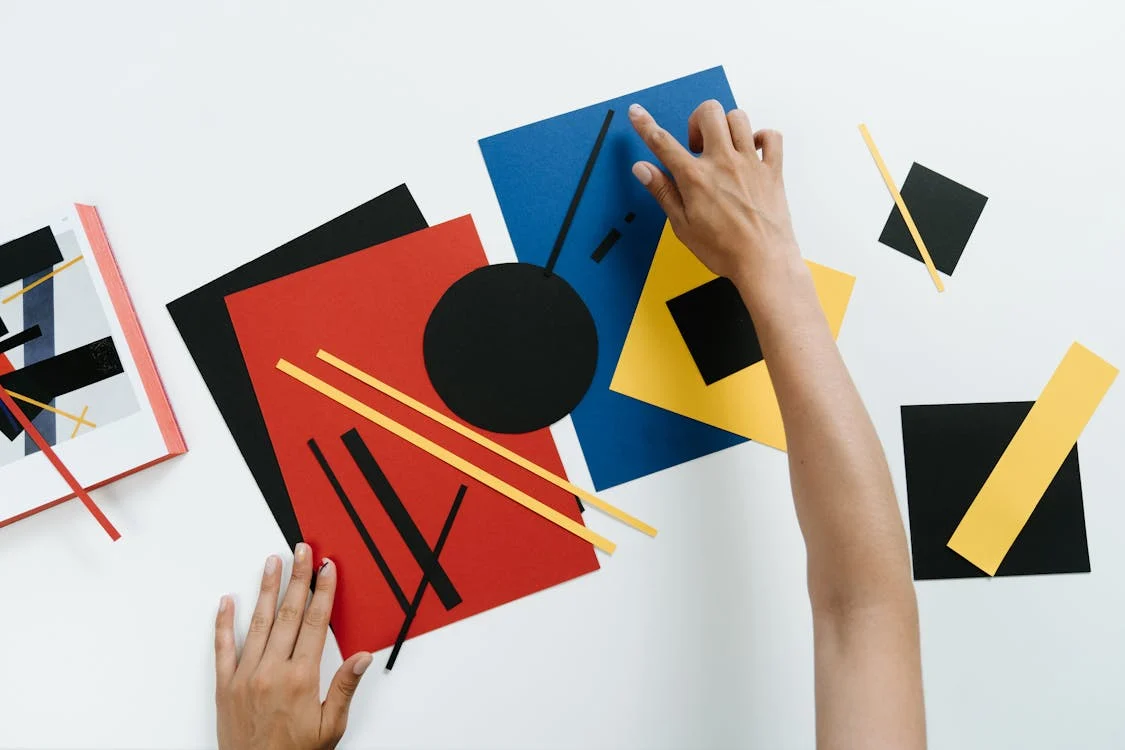
A short analysis: Why a Black Square Changed the Course of Art History In 1915, Kazimir Malevich exhibited a black square on a white canvas and declared: “I have transformed myself in the zero of form.” It was more than provocation — it was the birth of Suprematism, a movement that shattered centuries of representational art and set the stage for abstraction as we know it. What Is Suprematism? Suprematism is not just an aesthetic; it’s a philosophy. Malevich sought to liberate art from the burden of objects, representation, and narrative. His compositions — often made of geometric forms in pure color — were visual meditations on feeling, not function.…
What Makes a Painting Valuable to Collectors?
Understanding Rarity, Provenance, and Artistic Significance In the art world, value is rarely accidental. A painting’s worth emerges from a layered interplay of history, context, and perception — not just aesthetics. While taste is subjective, collectors who move with confidence typically understand five key drivers of value: 1. Artistic Significance Value begins with impact. Did the artist shift a movement, challenge convention, or redefine form? Consider Kandinsky’s early abstractions or Malevich’s Suprematist compositions — these works didn’t just reflect art history, they shaped it. 2. Rarity and Scarcity Scarcity enhances allure. Whether it’s a unique work or part of a limited series, the fewer there are, the more intense the…
The Jewish School of Paris: A Legacy of Artistic Innovation
The Jewish School of Paris, often referred to as part of the broader École de Paris, represents a vibrant chapter in the history of modern art. This group of artists, predominantly Jewish and of Eastern European origin, converged in Paris during the early 20th century, transforming the city into a global art hub. Their contributions not only enriched French art but also left an indelible mark on the development of Israeli art. Historical Context In the early 20th century, Paris became a magnet for artists from around the world, including many Jewish artists fleeing persecution in Eastern Europe. The term École de Paris was coined by André Warnod in 1925 to describe this…
Russian Avant-Garde
Exploring the Russian Avant-Garde: A Revolution in Art and Culture The Russian Avant-Garde was a groundbreaking movement that emerged in the early 20th century, roughly between 1890 and 1930. It encompassed a diverse array of artistic expressions, including painting, sculpture, literature, theater, and architecture. This vibrant period was marked by radical experimentation and a desire to break away from traditional forms, reflecting the turbulent social and political changes in Russia at the time. Origins and InfluencesThe movement drew inspiration from various sources, including Cubism, Futurism, and Expressionism in Western Europe. Russian artists sought to create a new visual language that would resonate with the revolutionary spirit sweeping across the country.…
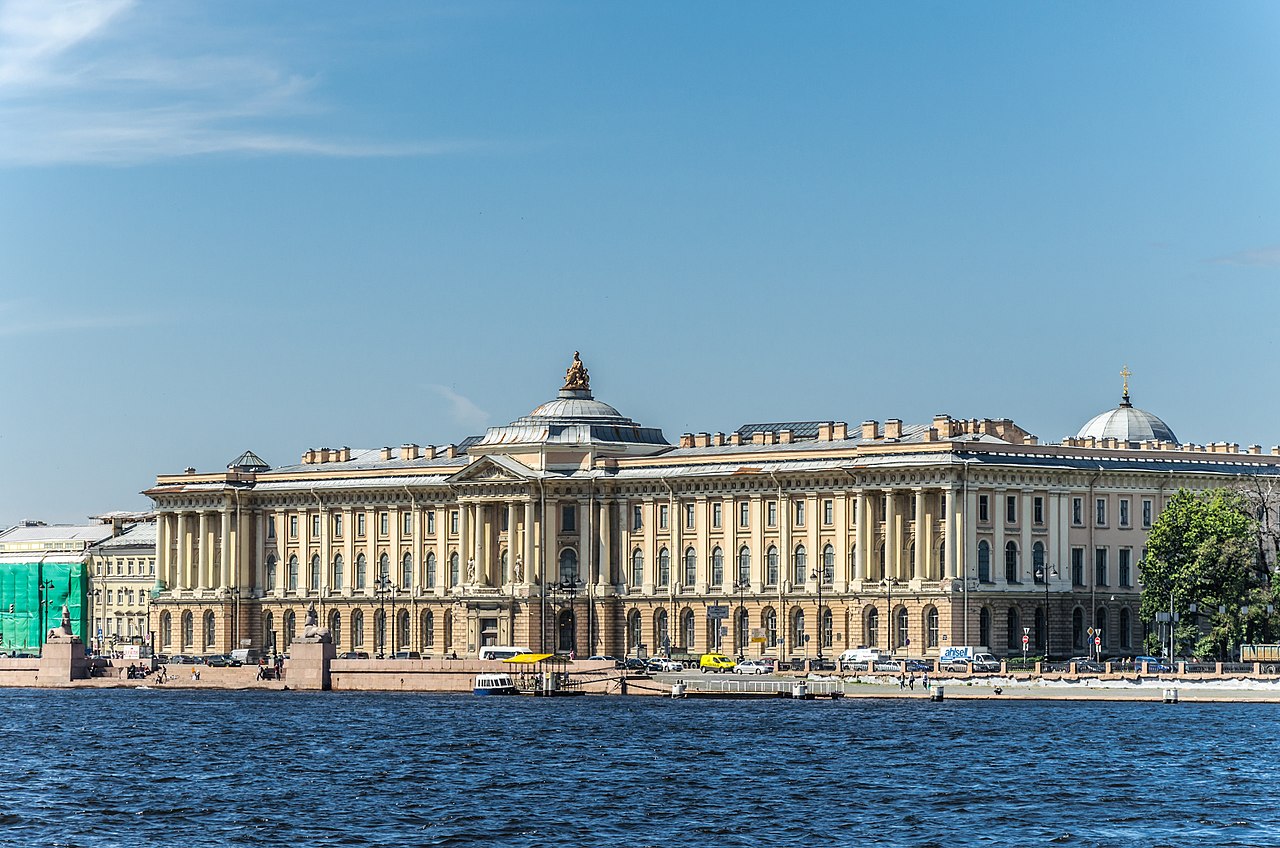
Leningrad School of Painting
On our websites you will find many paintings you may recognize as works of art inspired by The Leningrad School of Painting (Russian: Ленинградская школа живописи). This refers to a group of Soviet painters, who from 1930 to 1950 founded in Leningrad the Reformed Imperial Academy of Fine Arts, unified by the Leningrad Union of Soviet artists. The history of the Leningrad School covers the period from early 1930 to early 1990s. It’s appearance was the result of the conflict resolution and reflect predominant trends in the development of Soviet art and artisanship at the turn of the 1920-1930s. It was accelerated in April 1932 by political offices of the Central Committee of the Communist Party…
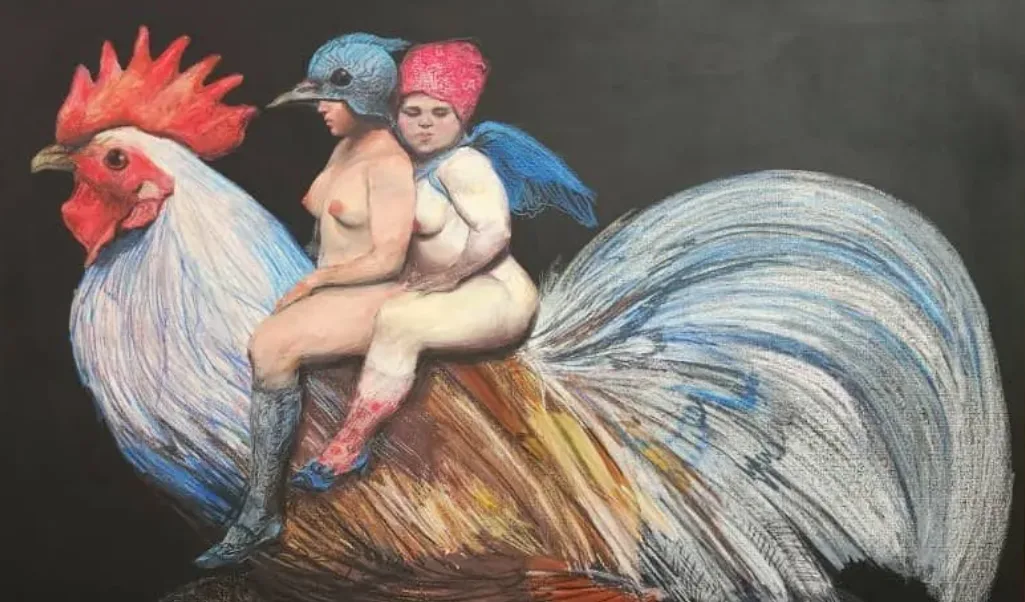
Unveiling the Transcendent Beauty: Malevich and the Russian Avant-Garde
Unveiling the Transcendent Beauty Introduction:Entering the realm of Kazimir Malevich and the Russian Avant-Garde is akin to embarking on a spiritual odyssey of artistic revelation. As an impassioned collector deeply enamored by Malevich’s oeuvre, one finds oneself irresistibly drawn to the ineffable allure and profound philosophical depths that characterize each stroke of his brush. In this essay, the narrative unfolds from the perspective of an ardent collector, eager to convey the enrapturing essence of Malevich’s graphic works, offering glimpses into the transcendent beauty that continues to captivate collectors and aficionados worldwide. The Russian Avant-Garde Movement:For those enthralled by the enigmatic allure of Malevich’s creations, the Russian Avant-Garde movement stands as…
Why is Wassily Kandinsky “The Rider” (1909) an important work?
Why is Wassily Kandinsky “The Rider” (1909) an important work? Around 1910, Kandinsky’s artistic style began to shift significantly towards abstraction. In 1910, he completed his first truly abstract watercolor, marking a pivotal moment in his career. This period also saw the publication of his influential book “Concerning the Spiritual in Art” in 1910, where he explored the spiritual dimensions of art and its connection to music. Kandinsky’s notable works from this era include “Composition I” (1910), which was unfortunately destroyed during World War II. His paintings increasingly emphasized emotion through color and form, moving away from traditional representation. In 1911, he co-founded the influential group Der Blaue Reiter, further…
Why would Kazimir Malevich shift away from Suprematism after the 1920’s?
Kazimir Malevich’s evolving relationship with Suprematism in the post-1920s era was influenced by a variety of factors, reflecting a complex interplay of political, personal, and philosophical dynamics. Politically, the ascent of Joseph Stalin’s regime in Soviet Russia marked a significant shift in cultural policies, favoring Socialist Realism as the sanctioned artistic style. Suprematism’s abstract, non-representational approach clashed with the regime’s preference for art that served propagandistic purposes and depicted idealized Soviet themes. Consequently, Malevich encountered mounting challenges in showcasing and disseminating his Suprematist works within the state-controlled artistic milieu. However, Malevich’s relationship with Suprematism was not solely defined by external pressures. Internally, he experienced a gradual evolution of his artistic…